Input script guide
This part gives a concise description for writing the input script of PFD-kit. The input parameter is very similar to that of DPGEN2, whose online documantation might also be useful.
Basics
Workflow host
PFD-kit is built upon the dflow package, which is in turn based on the Python API of ARGO workflow. Thus, one needs to specify the address of dflow host as well as the storage server for artifacts.
"dflow_config" : {
"host" : "http://address.of.the.host:port"
},
"dflow_s3_config" : {
"endpoint" : "address.of.the.s3.sever:port"
},
This is only neccesary when submitting to a custom server, there is no need to specify workflow server when running on Bohrium platform. Instead, one needs to input their Bohrium account details:
"bohrium_config": {
"username": "urname",
"password": "123456",
"project_id": 123456,
"_comment": "all"
},
The workflow would be then hosted on https://workflows.deepmodeling.com and the workflow progress can be accessed via https://workflows.deepmodeling.com/workflows.
Node setting
The one has to specify the computation resources, i.e., image and machine type for each step as PFD-kit executes computation tasks within each step via a docker container managed by the workflow host.
The default_step_config define the default step setting, for example:
"default_step_config": {
"template_config": {
"image": "registry.dp.tech/dptech/deepmd-kit:2024Q1-d23cf3e"
},
"executor": {
"type": "dispatcher",
"image_pull_policy": "IfNotPresent",
"machine_dict": {
"batch_type": "Bohrium",
"context_type": "Bohrium",
"remote_profile": {
"input_data": {
"job_type": "container",
"platform": "ali",
"scass_type": "c2_m4_cpu"}
}
}
}
},
The image entry in the template_config defines the image on which the container would be generated. The executor entry defines the machine and relevant parameters. In this case, a container node with two CPU core and 4GB memory would be instantiated via the Bohrium platform.
Similary, to set the step performing, say, the DFT calculation with ABACUS software, one can add the run_fp_config setting in the step_configs entry:
"step_configs": {
"run_fp_config": {
"template_config": {
"image": "registry.dp.tech/dptech/vasp:5.4.4",
},
"continue_on_success_ratio": 0.9,
"executor": {
"type": "dispatcher",
"image_pull_policy": "IfNotPresent",
"machine_dict": {
"batch_type": "Bohrium",
"context_type": "Bohrium",
"remote_profile": {
"input_data": {
"job_type": "container",
"platform": "ali",
"scass_type": "c32_m64_cpu"}}}}}
}
One can see that the VASP image and a more powerful machine with 32 cores and 64GB memories are selected.
Fine-tune task
A model fine-tune workflow is defined by the following paramters. One first specifies the workflow type in the task section,
which is finetune in this case.
"task":{
"type":"finetune"
}
The inputs section includes essential user input parameters. Here one needs to specify type_map, which maps the type embedding of pretrained model
to corresponding element name. The path to pretrained base model also needs to be provided.
"inputs":{
"type_map":["Li","..."],
"base_model_path":["path_to_base_model"]
}
The conf_generation section defines how perturbed structures are generated from initial structure files. Multiple input structure files can be
present in the init_configuration sub-section, and the pert_generation defines the rule for generating perturbed structures.
"conf_generation":{
"init_configurations":{
"type": "file",
"fmt": "vasp/poscar",
"files": ["LGPS.vasp"]
},
"pert_generation":[{
"conf_idx": "default",
"atom_pert_distance":0.15,
"cell_pert_fraction":0.03,
"pert_num": 5}]
}
The exploration section defines the parameters for molecular dynamics (MD) simulations, which iteratively add new data to the fine-tune training set. In this example, the MD exploration is performed using the LAMMPS package. Multiple exploration stages can be specified, each executed sequentially. Within each stage, various task groups with different settings can be defined. In this case, the workflow consists of a single stage with one task group.
"exploration": {
"type": "lmp",
"config": {"command": "lmp -var restart 0"},
"stages":[[
{ "_comment": "group 1 stage 1 of finetune-exploration",
"conf_idx": [0],
"n_sample":3,
"exploration":{
"type": "lmp-md",
"ensemble": "npt",
"dt":0.005,
"nsteps": 2000,
"temps": [500],
"press":[1],
"trj_freq": 200},
"max_sample": 10000}]
],
"max_iter":2,
"convergence":{
"type":"energy_rmse",
"RMSE":0.01},
"filter":[{"type":"distance"}]
}
Within the task group settings, you define the configuration index number, the number of samples, simulation temperatures, pressures, time step, number of simulation steps, etc. In the mentioned task group, each MD simulation starts from 3 randomly chosen frames of the perturbed structures of the first initial configuration, as indicated in the conf_idx setting.
The fp part sets the first principle calculation. Detailed parameters can be referenced in the DPGEN2 documentation. Below is an example configuration for running VASP:
"fp": {
"type": "fpop_abacus",
"task_max": 50,
"extra_output_files:":[],
"run_config": {
"command": "source /opt/intel/oneapi/setvars.sh && mpirun -n 32 vasp_std"
},
"inputs_config": {
"incar": "INPUT.scf",
"pp_files": {
"Li": "POTCAR-Li",
"S":"POTCAR-S",
"Ge": "POTCAR-Ge",
"P": "POTCAR-P"
}}
}
You need to specify the path to the ABACUS input file and the pseudopotential file for each element. The ABACUS command should be configured according to the machine type for optimal performance.
The train section defines the type of pretrained model and the specific training configuration. The detailed training script can be provided either as a dict or in an additional script (as shown below). It is crucial to provide the path to the pretrained model in the init_models_paths entry.
"train": {
"type": "dp",
"config": {
"impl": "pytorch",
"init_model_policy": "no",
"init_model_with_finetune":true,
},
"template_script": "train.json",
"init_models_paths":["OpenLAM_2.1.0_27heads_2024Q1.pt"],
}
Distillation task
The input script for tdistillation is actually very similar to that of fine-tune, but there all a few difference:
"task":{"type":"dist"},
"inputs":{
"type_map":["..."],
"teacher_model_path":"path_to_teacher_model",
"teacher_model_style":"dp"
},
"conf_generation":{...},
"train":{
"type": "dp",
"config": {
"init_model_policy": "no",
},
"template_script": "train.json"
},
"exploration":{
...,
"test_set_config":{
"test_size":0.2
}
},
"inference":{
"max_force":10.0
}
You need to specify the teacher model style and path to the teacher model file at the inputs part. The relevant setting in the training configuration also needs to be modified, as the distilled model is essentially a simpler model trained from scratch instead of fine-tune.
A new entry test_set_config would be available in the exploration section, this setting determines how many labeled frame would serve as the test set (20 % in this case). Moreover, you can add additional parameters into the inference section, where configurations with excess atomic forces would be filtered out.
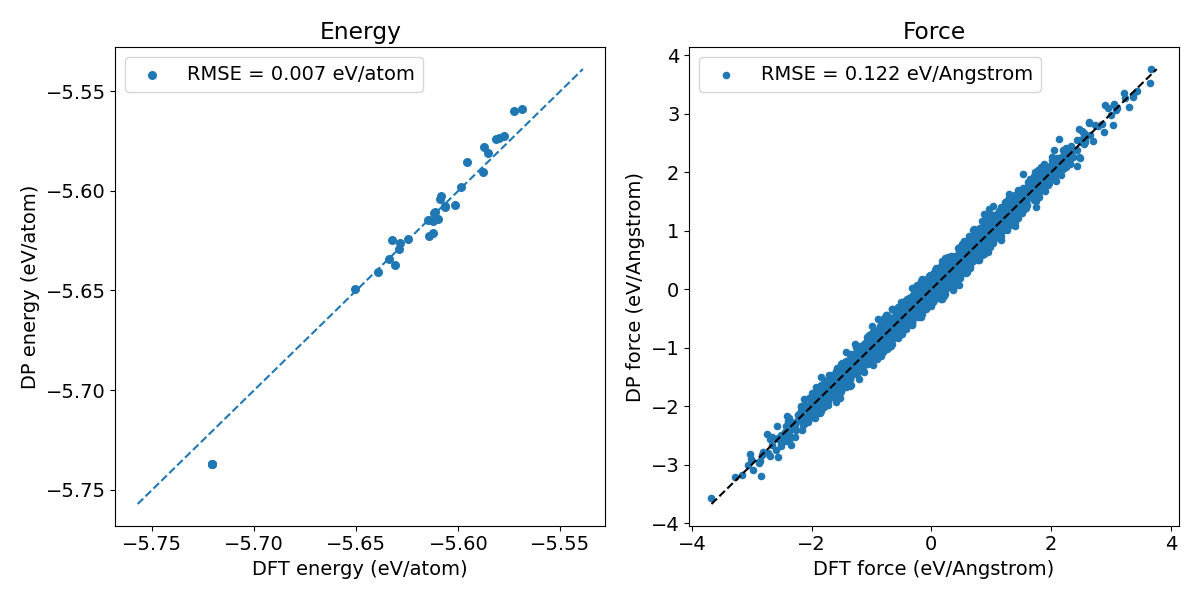
Figure 1. Prediction error of pretrained DPA-2 models on crystal Si.
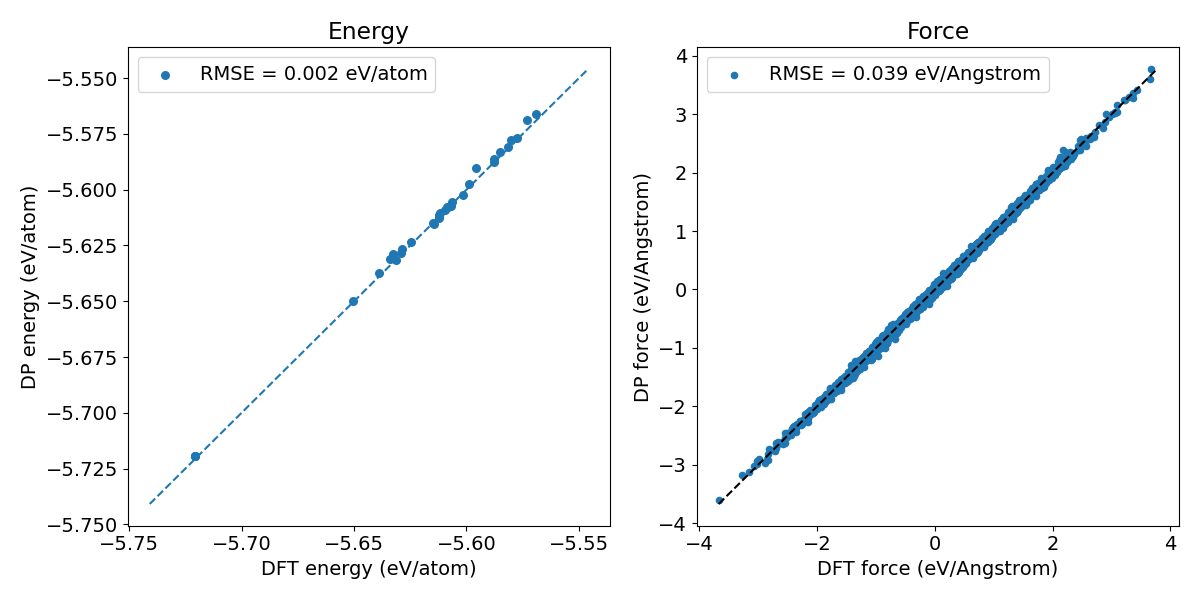
Figure 2. Prediction error of the fine-tuned Si model.
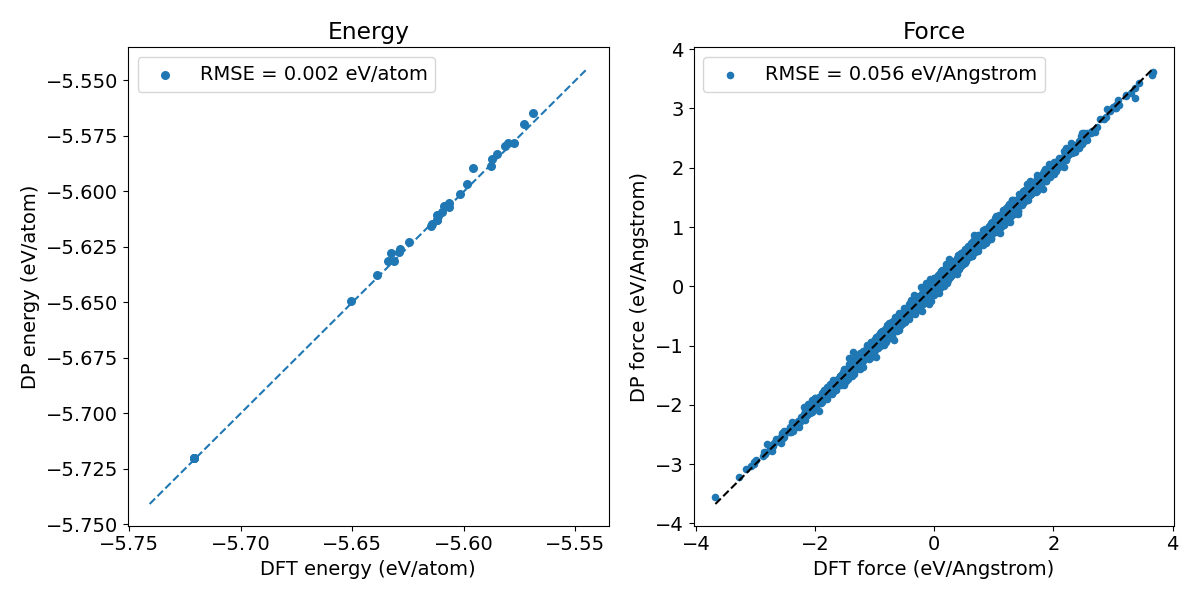
Figure 3. Prediction error of the Si model generated through knowledge distillation.